Have you ever wondered why a bat isn’t called a bird, even though it flies? It’s easy to think of bats as just another type of bird because they share one key trait—flight.
But there’s much more to the story. Understanding why bats are different from birds can change the way you see the animal world around you. Keep reading, and you’ll discover surprising facts that will make you question everything you thought you knew about these mysterious creatures.
Your curiosity is about to pay off!

Credit: www.batcon.org
Bat Classification
Bats belong to the class of mammals, not birds. They have furcovering their bodies, unlike birds that have feathers. Bats give birth to live young and feed them with milk. Birds, on the other hand, lay eggs.
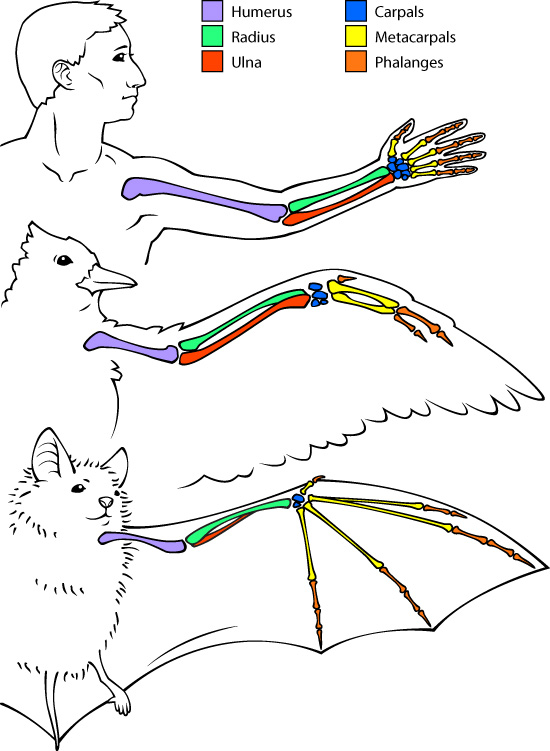
Bats have warm bloodand breathe using lungs, just like mammals. Their wings are made of skin stretched over long fingers, differing from bird wings that have feathers and bones. Bats also have teeth, while many birds do not.
| Feature | Bat | Bird |
|---|---|---|
| Body Covering | Fur | Feathers |
| Birth | Live young | Eggs |
| Wings | Skin over fingers | Feathers over bones |
| Feeding Young | Milk | No milk |
Credit: askabiologist.asu.edu
Physical Features
Bats have fur and flexible wings made of skin stretched over bones, unlike birds with feathers and rigid wings. Their wing structure helps them fly differently from birds. These physical traits show why bats are mammals, not birds.
Wing Structure
Bats have wings made of thin skin stretched over long finger bones. Birds’ wings are covered with feathers. This skin allows bats to move their wings more flexibly. Birds flap their wings differently due to their feathered structure.
Body Covering
Bats are covered with fur, similar to mammals. Birds have feathers all over their bodies. Fur helps bats stay warm at night. Feathers help birds fly and keep warm during the day.
Skeletal Differences
| Feature | Bat | Bird |
|---|---|---|
| Finger Bones | Very long, support wing skin | Short, support feathers |
| Bone Type | Flexible and light | Hollow and lightweight |
| Tail | Short and furry | Long and feathered |
Reproduction And Development
Bats give live birth, unlike birds that lay eggs. This is a key difference between them.
Mother bats nurse their youngwith milk. Birds do not feed their babies this way.
Bat babies are born alive and grow inside the mother. Birds hatch from eggs outside the body.
- Bats have mammary glandsto feed their babies.
- Birds feed young with regurgitated foodor insects.
- Bat babies stay close to their mothers for warmth and milk.
- Bird chicks rely on nests and parents to keep them safe.
Credit: www.dairynewsaustralia.com.au
Flight Mechanism
Bats fly using flexible skin stretched over their fingers, unlike birds with feathers and rigid wings. This unique flight style shows bats are mammals, not birds. Their wing structure helps them maneuver quickly in the air.
Wing Anatomy
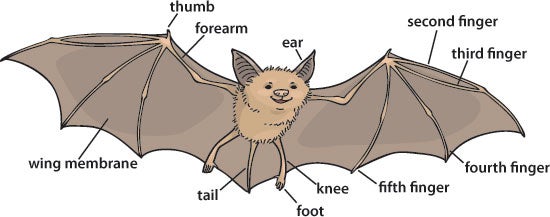
Bats have unique wings. Their wings look like human hands. Fingers stretch the wing skin. This makes them different from birds. Birds have feathers. Bats have skin. This helps bats fly in dark places. Their wings are flexible. Flexibility helps bats turn quickly. Birds cannot do this as well. Bats use their thumbs. Thumbs help them climb and hang.
Flight Patterns
Bats fly differently than birds. They flap their wings in a special way. Wing flaps are slower. Slow flaps help bats hover. Hovering helps in catching bugs. Birds fly straight most times. Bats fly zigzag and loop. Zigzag helps avoid obstacles. Bats can fly backwards too. Backward flight is rare in birds. Their flight is silent. Silence helps them hunt quietly.
Sensory Abilities
Bats use echolocation to navigate and find food in the dark, unlike birds that rely mostly on sight. This unique sensory ability sets bats apart from birds. Their hearing and sound skills make them special mammals, not flying birds.
Echolocation
Bats use echolocationto find food and move around in the dark. They send out sound waves that bounce off objects. The echoes help bats know where things are. This skill is unique to bats and some sea animals. Birds do not have this ability.
Vision And Hearing
Bats have good hearingand use it more than their eyes. Their eyes are small and not very strong. Many bats can see in low light but not as well as birds. Birds rely mostly on their sharp visionto find food and fly.
Evolutionary History
Bats are mammals, not birds. They belong to a group called Chiroptera. They have fur, give live birth, and feed milk to their babies. These are key mammal traits.
Birds evolved from dinosaurs long ago. They have feathers, lay hard eggs, and have beaks without teeth. Birds and bats look alike because both can fly, but their bodies are very different.
| Feature | Bats (Mammals) | Birds |
|---|---|---|
| Body Covering | Fur | Feathers |
| Reproduction | Live birth, feed milk | Lay eggs |
| Flight | Membranous wings (skin stretched over fingers) | Feathered wings |
| Skeleton | Flexible bones, mammal structure | Hollow bones, bird structure |
Frequently Asked Questions
Why Is A Bat Not Classified As A Bird?
Bats are mammals, not birds. They have fur, give birth to live young, and nurse with milk.
How Do Bats’ Wings Differ From Bird Wings?
Bat wings have skin stretched over fingers, while bird wings have feathers on bones.
Do Bats And Birds Have Different Flying Abilities?
Bats can fly with flexible wings and echolocate, unlike birds that rely on feathers and sight.
Conclusion
Bats are often mistaken for birds because they fly. But bats are mammals, not birds. They have fur, not feathers. They give birth to live babies, unlike birds that lay eggs. Bats use echolocation to find food, a skill birds don’t have.
Knowing these facts helps us understand nature better. Next time you see a flying bat, remember it’s a unique creature. Not a bird, but a special mammal of the night. This makes bats fascinating and important to learn about.